ArrayList<Integer[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
위와 같이 Integer[] 배열을 요소로 갖는 ArrayList에서 배열의 첫 번째 요소를 기준으로 정렬하고자 한다.
Collections.sort() 사용
Comparator 선언으로 정렬
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c)
첫 파라미터에는 정렬할 리스트를, 두 번째 파라미터에는 새로운 Comparator를 생성해 넣어준다.
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer[] o1, Integer[] o2) {
return o1[0] - o2[0];
}
});
int compare(T o1, T o2)
Comparator의 compare 메서드를 오버라이딩해 선언한다. Integer[] 배열을 파라미터로 받아 두 배열의 첫 번째 요소를 비교해 오름차순으로 반환하도록 하였다.
람다식으로 Comparator 생성을 대체
Collections.sort(list, (o1, o2) -> o1[0] - o2[0]);
Comparator.comparingInt로 람다식을 대체
Collections.sort(list, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[0]));
List.sort() 사용
default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c)
java 1.8부터는 list에서도 sort 메서드를 지원한다. Collection.sort와 동일한 방식으로 Comparator를 적용한다.
list.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[0]));
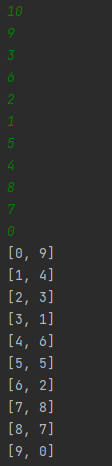
실행 확인
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
ArrayList<Integer[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
//list에 값 추가
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
list.add(new Integer[]{Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()), i});
}
//정렬
list.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o[0]));
//정렬 결과 확인
for (Integer[] integers : list) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(integers));
}
정렬 기준 인덱스 변경
• 리스트의 배열 인덱스 0을 기준으로 정렬하고자 해서 o[0]과 같이 사용하였다. 다른 인덱스를 기준으로 정렬을 원할 경우 [] 안의 값을 바꿔준다.
내림차순 정렬을 원할 경우
• 내림차순 정렬을 원할 경우 sort 메서드가 사용된 코드 부분을 다음과 같이 수정한다.
list.sort((o1, o2) -> o2[0] - o1[0]);
ref.
Sort List of arrays according to specific array elements
I have a List of arrays where the fifth element of each array (array[4]) is of type Date and the fourth element of each array (array[3]) is of type String. I am trying to sort the List according to...
stackoverflow.com
Collections (Java SE 11 & JDK 11 )
Rotates the elements in the specified list by the specified distance. After calling this method, the element at index i will be the element previously at index (i - distance) mod list.size(), for all values of i between 0 and list.size()-1, inclusive. (Thi
docs.oracle.com
Comparator (Java SE 11 & JDK 11 )
Compares its two arguments for order. Returns a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the first argument is less than, equal to, or greater than the second. The implementor must ensure that sgn(compare(x, y)) == -sgn(compare(y, x)) for all x and
docs.oracle.com
Comparator (Java SE 11 & JDK 11 )
Compares its two arguments for order. Returns a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the first argument is less than, equal to, or greater than the second. The implementor must ensure that sgn(compare(x, y)) == -sgn(compare(y, x)) for all x and
docs.oracle.com
List (Java SE 11 & JDK 11 )
An ordered collection (also known as a sequence). The user of this interface has precise control over where in the list each element is inserted. The user can access elements by their integer index (position in the list), and search for elements in the lis
docs.oracle.com
'p-languages > java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| java/ Integer를 '==' 연산자가 아닌 'equals' 메서드로 비교해야 하는 이유 (Integer Cache) (0) | 2022.11.11 |
|---|---|
| java/ 8 또는 12 길이의 int 배열을 받아 전화번호 형식의 String으로 반환하기 (0) | 2022.06.06 |
| java/ 내부 클래스의 종류와 내부 클래스를 사용함으로써 얻는 장점 (0) | 2022.05.23 |
| java/ Stream 중간 처리 메서드 - filtering, mapping, sorting, looping (0) | 2022.05.23 |
| java/ String.contains() : 문자열에 특정 부분 문자열이 있는지 확인하는 메서드 (0) | 2022.05.17 |
